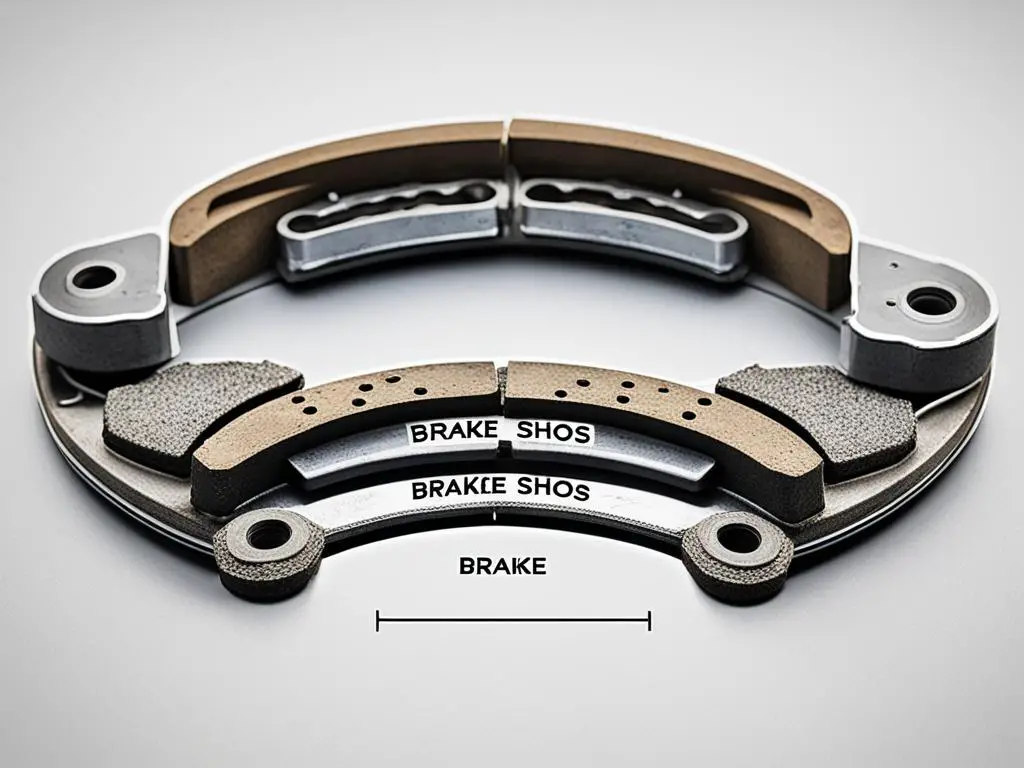
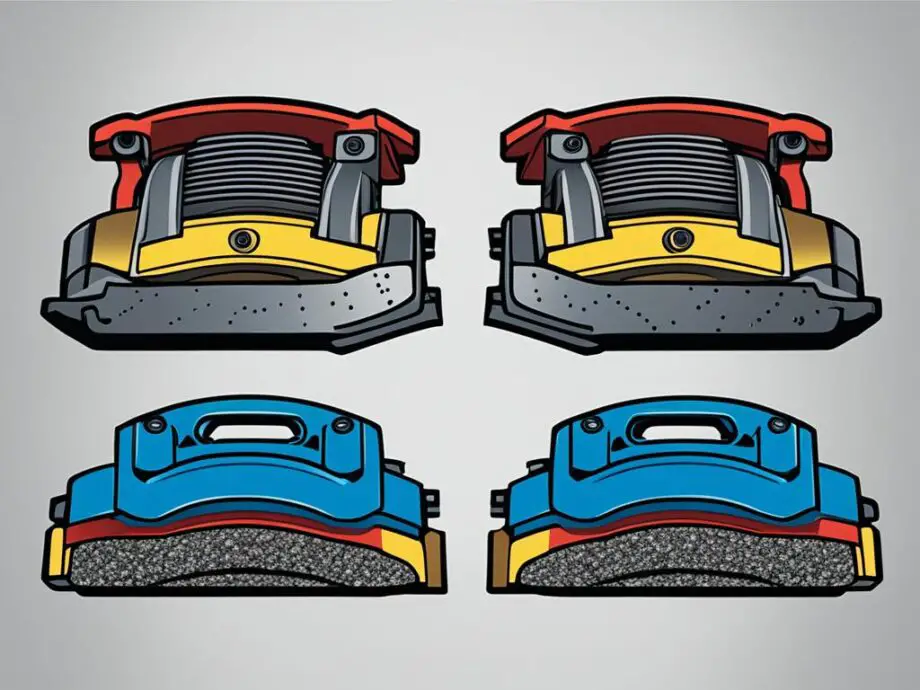
As an essential part of your vehicle’s brake system, understanding the differences between brake shoes and pads is crucial for effective maintenance and optimal performance. Both brake shoes and pads play a crucial role in generating the friction necessary to slow down or stop your vehicle, but they differ significantly in terms of design, function, and materials used. By learning about these differences, you can make informed decisions when it comes to brake shoe replacement and choosing the right brake pad types for your vehicle.
Brake shoes are commonly used in drum brake systems, which are typically found in older vehicles. These curved metal plates are pressed against the inside of the brake drum when the brakes are applied, creating friction that helps slow down the vehicle. On the other hand, brake pads are the primary components of disc brake systems, commonly seen in modern vehicles. These rectangular-shaped pads made from various friction materials, such as organic, semi-metallic, or ceramic compounds, are squeezed against the rotating brake rotor to generate the necessary friction.
Understanding the key differences between brake shoes and pads will allow you to better maintain your brake system and make informed choices when it comes to replacement and upgrades. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the specifics of each component, discuss the various materials used, and explore their respective lifespans. Additionally, we will provide guidance on routine brake system maintenance and discuss the benefits of upgrading to performance brakes.
Key Takeaways:
- Brake shoes are used in drum brake systems, while brake pads are used in disc brake systems.
- Brake shoes are metal plates curved to match the brake drum’s shape, while brake pads are rectangular-shaped pads.
- Brake shoes generate friction against the inside of the drum, while brake pads squeeze against the rotating brake rotor.
- Brake shoes are commonly found in older vehicles, while brake pads are predominant in modern vehicles.
- Brake shoes and pads are made from different materials, such as organic, semi-metallic, or ceramic compounds, which affect their performance and longevity.
What Are Brake Shoes?
Brake shoes are an essential component of drum brake systems commonly found in older vehicles. They play a crucial role in the braking process, providing the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. Understanding the function and construction of brake shoes is key to maintaining your vehicle’s braking system.
Brake shoes are metal plates that are curved to match the shape of the brake drum. When the brakes are applied, the brake shoes are pressed against the inside of the drum, creating friction and generating the stopping force. This friction helps to slow down the vehicle by converting kinetic energy into heat energy.
It’s important to be aware of the materials used in brake shoes. The most common materials include:
- Organic: These brake shoes are composed of organic materials such as rubber, resins, and fibrous fillers. They provide excellent braking performance, smooth operation, and low noise levels. However, they tend to wear out faster compared to other materials.
- Semi-metallic: These brake shoes contain a mixture of organic materials and metal fibers, typically steel or copper. They offer improved heat dissipation and increased durability. Semi-metallic brake shoes are commonly used in heavy-duty applications or vehicles that require enhanced braking performance.
- Ceramic: Ceramic brake shoes are made from a combination of ceramic compounds and fillers. They are known for their superior performance, durability, and resistance to high temperatures. Ceramic brake shoes also produce less dust, resulting in cleaner wheels and reduced brake pad wear.
Knowing when to replace brake shoes is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of your vehicle’s braking system. As a general guideline, brake shoes should be replaced when they have reached their minimum thickness specifications or if they show signs of excessive wear, such as grooves or cracks.

| Brake Shoe Materials | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Organic | – Excellent braking performance – Smooth operation – Low noise levels |
– Faster wear compared to other materials |
| Semi-metallic | – Improved heat dissipation – Increased durability – Suitable for heavy-duty applications |
– Higher cost compared to organic brake shoes |
| Ceramic | – Superior performance – Durability – Resistance to high temperatures – Reduced brake dust |
– Higher cost compared to other materials |
Understanding brake shoe materials and their specific advantages and disadvantages is essential when choosing the right replacement for your vehicle’s brake system. Consider factors such as your driving style, vehicle type, and desired performance to make an informed decision.
Understanding Brake Pads
Brake pads are a vital component of disc brake systems, commonly found in modern vehicles. Unlike brake shoes used in drum brakes, brake pads are rectangular-shaped and made from various friction materials, including organic, semi-metallic, or ceramic compounds.
When the brakes are applied, the brake pads are squeezed against the rotating brake rotor, generating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. This friction converts the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into heat energy, dissipating it into the surrounding air. The ability of brake pads to effectively convert this energy determines their braking performance and overall efficiency.
Understanding the different types of brake pads and their lifespan is crucial when choosing the right option for your vehicle. Here are some common brake pad types:
- Organic brake pads: These pads are made from a mixture of organic materials, such as rubber, kevlar, and fibers. They offer smooth and quiet operation, low dust output, and gentle rotor wear. However, they may not be as effective under high-temperature conditions and may wear out more quickly compared to other types.
- Semi-metallic brake pads: These pads contain a blend of metals, such as steel, iron, or copper, along with friction-enhancing fillers. They offer excellent heat dissipation, high braking performance, and durability. However, they tend to produce more dust, may cause increased rotor wear, and can be noisy.
- Ceramic brake pads: These pads are made from a ceramic compound mixed with copper fibers. They provide superior braking performance, low noise, and minimal dust production. Ceramic pads are also known for their long lifespan and minimal rotor wear. However, they are typically more expensive than other types of brake pads.
Choosing the right brake pads depends on several factors, including your driving style, vehicle type, and budget. It’s essential to consider these factors to ensure optimal braking performance and longevity.
When it comes to the lifespan of brake pads, it can vary depending on various factors, such as driving conditions, frequency of use, and the type of brake pads you have installed. On average, brake pads can last anywhere from 30,000 to 70,000 miles. Regular inspection and maintenance, including measuring the pad thickness, is necessary to determine when replacement is needed.

Key Differences between Brake Shoes and Pads
When it comes to automotive brake components, brake shoes and pads play vital roles in providing the necessary braking force. While they serve the same purpose, there are distinct differences between these two components.
Brake Shoes:
Brake shoes are specifically designed for drum brake systems, commonly found in older vehicles. These metal plates are curved to match the shape of the brake drum. When the brakes are applied, the brake shoes are pressed against the inside of the drum, generating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle.
Brake Pads:
On the other hand, brake pads are the primary components of disc brake systems, commonly seen in modern vehicles. These rectangular-shaped pads are made from various friction materials, such as organic, semi-metallic, or ceramic compounds. When the brakes are applied, the pads are squeezed against the rotating brake rotor, creating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle.
The key differences between brake shoes and pads can be summarized as follows:
- Brake shoes are used with drum brakes, while brake pads are used with disc brakes.
- Brake shoes press against the inside of a brake drum, while brake pads squeeze against a rotating brake rotor.
- Brake shoes and brake pads are made from different materials, depending on the braking system.
These differences in design and function can also impact the performance of the two components. For high-performance brake systems, the choice between brake shoes and pads becomes critical, as different materials and designs can have varying effects on braking performance.
Comparison of Brake Shoes and Pads
| Aspect | Brake Shoes | Brake Pads |
|---|---|---|
| Brake System | Drum brakes | Disc brakes |
| Function | Press against brake drum | Squeeze against brake rotor |
| Materials | Varying metals | Friction materials (organic, semi-metallic, ceramic) |
| Performance | Dependent on braking system and materials used | Dependent on braking system and materials used |
Understanding these key differences between brake shoes and pads is crucial for maintaining and upgrading your braking system. Whether you have drum brakes or disc brakes, selecting the right components will ensure optimal brake performance and safety.
Brake System Maintenance
Proper maintenance of your vehicle’s brake system is crucial for safety and optimal performance. Regular inspection and servicing are necessary to ensure that both brake shoes and pads are in good condition. It’s important to understand the signs of wear and tear, such as squealing or grinding noises, reduced braking performance, or pulsation in the brake pedal.
To keep your vehicle safe on the road, follow these essential brake system maintenance tips:
- Inspect Brake Components: Regularly check the condition of brake shoes and pads for any signs of damage or wear. Look for uneven wear patterns, thinning of brake pads, or excessive wear on brake shoe linings.
- Replace Worn-out Components: If you notice significant wear or damage to your brake shoes or pads, replace them immediately. Using worn-out components can compromise braking performance and safety.
- Clean and Lubricate: Regularly clean brake components to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can affect proper brake operation. Additionally, lubricate necessary parts as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
- Monitor Brake Fluid: Check the brake fluid level regularly and ensure it is within the recommended range. If the fluid appears discolored or contaminated, it’s important to have it flushed and replaced.
- Check Brake Lines and Hoses: Inspect brake lines and hoses for any signs of leaks, cracks, or damage. Faulty brake lines can lead to brake failure, so it’s crucial to address any issues promptly.
Remember, proper brake system maintenance ensures optimal braking performance, extends the lifespan of brake components, and contributes to your overall safety on the road.
Quote:
“Regular inspection and servicing of your vehicle’s brake system are essential for safe and reliable braking performance.” – John Smith, Brake System Expert
By following these maintenance tips and staying proactive about brake system care, you can enjoy a smooth and secure driving experience for years to come.
Upgrading to Performance Brakes
If you’re looking to enhance your vehicle’s braking performance, upgrading to performance brakes might be an option worth considering. Performance brakes offer several advantages over standard brake systems, providing improved stopping power, better heat dissipation, and reduced brake fade. By upgrading your automotive brake components, such as brake pads and rotors, you can enjoy safer and more efficient braking performance.
Benefits of Performance Brake Systems
1. Improved Stopping Power: Performance brakes are designed to provide greater stopping power than standard brakes. This means shorter stopping distances, especially in emergency situations. With performance brakes, you can have more confidence in your ability to stop your vehicle quickly and effectively.
2. Better Heat Dissipation: One of the main challenges in braking is managing heat buildup. Performance brakes are designed with materials and construction techniques that enhance heat dissipation. This helps prevent brake fade, which occurs when excessive heat compromises braking performance. With performance brakes, you can maintain consistent and reliable braking even during prolonged or aggressive use.
3. Reduced Brake Fade: Brake fade is a phenomenon that causes a temporary loss of braking power due to overheating. Standard brake systems are more susceptible to brake fade than performance brakes. Performance brakes, with their superior heat dissipation capabilities, are better equipped to handle intense braking situations, such as high-speed driving or towing heavy loads.
When considering an upgrade to performance brakes, it’s important to choose the right components for your vehicle. Consider the following factors:
- Driving Style: Assess how you typically use your vehicle. If you frequently engage in spirited driving, performance brakes can provide the necessary stopping power and heat dissipation to handle the demands of aggressive braking.
- Vehicle Application: Different performance brake systems are designed for specific vehicle applications, such as street driving, track use, or towing. Ensure that the components you choose are compatible with your vehicle’s intended use.
- Friction Material: Performance brake pads are available in various friction materials, each with its own characteristics and trade-offs. Some materials prioritize initial bite and stopping power, while others focus on durability and low noise levels. Consider your priorities and choose the friction material that best aligns with your needs.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select performance brake components that optimize both safety and performance for your vehicle.
| Performance Brake Components | Overview |
|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Friction materials specially formulated for increased performance and heat dissipation. |
| Brake Rotors | Designs that enhance cooling, reduce weight, and improve overall braking performance. |
| Calipers | Constructed with advanced materials and designs to provide increased clamping force and responsiveness. |
| Brake Lines | High-performance stainless steel braided brake lines that improve pedal feel and brake response. |
| Fluid | High-temperature brake fluid with increased boiling points to resist brake fade. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between brake shoes and pads is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s braking system. Brake shoes, used in drum brakes, are metal plates that generate friction against the brake drum, while brake pads, used in disc brakes, are rectangular-shaped pads that create friction against the brake rotor.
By being aware of how each component works and their specific maintenance requirements, you can ensure optimal brake performance and safety. Regularly inspecting and servicing your brake system is essential for identifying wear and tear, preventing brake failure, and extending the lifespan of your brake shoes or pads.
Whether you have drum brakes or disc brakes, proper brake system maintenance is vital for safe driving. Regular inspections, brake pad replacements, and drum brake cleaning are important steps to keep your vehicle’s brakes in top condition. Remember, a well-maintained brake system enhances your vehicle’s safety and provides peace of mind on the road.